BP09B – Consumer receives a data processing service on a data resource via an application
To help understand the content of this document, readers should familiarize themselves with the key definitions and actors.
Overview
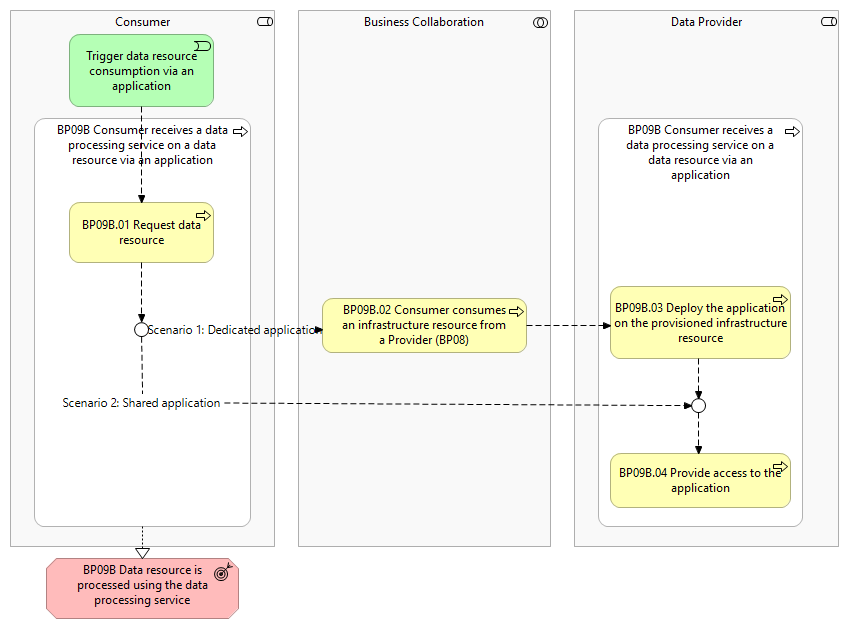
This business process covers the situation where a Consumer has a usage contract for a certain data resource, and seeks to process that data resource via an application provided by a Data Provider. This enables a Consumer to access an application that offers restricted viewing (such as read only) or processing capabilities on the data resource in two possible scenarios:
Scenario 1: A stand-alone application deployed on a dedicated infrastructure resource per Consumer
In this scenario, the Data Provider provisions dedicated infrastructure for each Consumer, hereby deploying an application that has access to the data source, and which can use its processing capabilities on the data source. The Consumer only receives access to the application endpoints (e.g., web interface), allowing them to perform various processes on the data source, such as data analysis.
Scenario 2: Shared access to an existing application
In this scenario, deploying a dedicated application for each Consumer is not feasible (e.g., due to expensive licensing) or not the preferred solution for the Data Provider. Instead, the Consumer gains access to an existing application. The type of access depends on the Application and the Data Provider and is not controlled by Simpl-Open (it is beyond what is indicated in the contract). For instance, the application may have its own identity and access management system, allowing the creation of new user accounts for a Consumer or the provision of temporary access.
It includes the following main steps:
- Request data resource: The Consumer initiates the process by requesting a specific data resource from the Data Provider. This request is based on the information found in the data space catalogue, which was previously searched and identified by the Consumer.
- Consumer consumes an infrastructure resource from a Provider: In the case of a dedicated application (scenario 1), an infrastructure resource is provisioned in collaboration between the Consumer and Data Provider with the aim of deploying the the application.
- Deploy the application on the provisioned infrastructure: In the case of a dedicated application (scenario 1), the Data Provider deploys a dedicated application on the provisioned infrastructure resource. The deployment occurs automatically via the infrastructure provisioning mechanism, and the deployment script that is linked to the service offering / usage contract.
- Provide access to the application: The Data Provider applies the access control rules and provides the Consumer with the right access credentials.
Actors
The following actors are involved:
- Consumer
- Data Provider
Assumptions
No specific assumptions are made for this business process.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be fulfilled:
- Dataspace is configured: The Governance Authority has configured the data space catalogue with the corresponding vocabulary and schemas to have the general structure of a resource description, contract clauses, and other vital components (Business Process 2).
- Consumer / Data Provider onboarded: Both the Consumer and Data Provider must complete the onboarding process (Business Process 3A) before they can consume or provide any available resources.
- End-User authenticated & authorised: The End-User is authenticated and has the appropriate role and permissions to perform the steps in the process (Business Process 3B).
- Resource description is present in the data space catalogue: A resource description must be published in the data space catalogue for the Consumer to find a resource in the data space catalogue (Business Process 5). As such, it is assumed that the Consumer has searched in the data space catalogue and found the resource description (Business Process 6).
- Usage contract established for the data resource: The Consumer can consume the data resource according to the terms and conditions of the usage contract (Business Process 7).
Details
The following shows the detailed business process diagram and gives the step descriptions.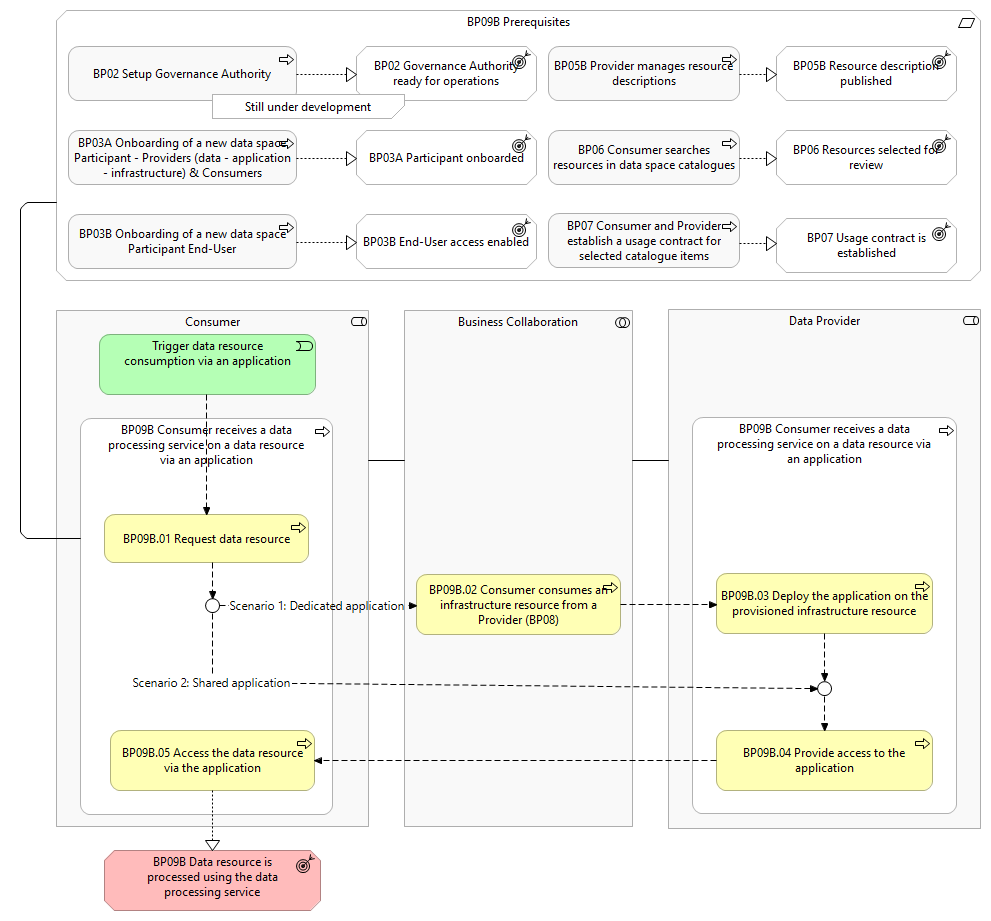
Trigger data resource consumption via an application
The Consumer initiates the process to consume a data resource via an application from a Data Provider.
BP09B.01 Request data resource
The Consumer initiates the process by requesting a specific data resource from the Data Provider. This request is based on the information found in the data space catalogue, which was previously searched and identified by the Consumer.
BP09B.02 Consumer consumes an infrastructure resource from a Provider (BP08)
An infrastructure resource is provisioned in collaboration between the Consumer and Data Provider with the aim of deploying the the application.
BP09B.03 Deploy the application on the provisioned infrastructure resource
The Data Provider deploys a dedicated application on the provisioned infrastructure resource. The deployment occurs automatically via the infrastructure provisioning mechanism, and the deployment script that is linked to the service offering / usage contract.
BP09B.04 Provide access to the application
The Data Provider configures and applies the access control rules, and provides the Consumer with the right access credentials:
- Scenario 1: Access is granted automatically in the post configuration process, depending on the type and capabilities of the application.
- Scenario 2: Access is granted outside the scope of Simpl-Open, and may be done manually or automatically. Additionally, the provisioning or use of an infrastructure outside the boundary of the data space is probable, and is hence not be controlled by Simpl-Open.
BP09B.05 Access the data resource via the application
The Consumer consumes the data resource via the application.
Outcomes
- Data resource is processed using the data processing service: The Consumer accesses and consumes a data resource via an application provided by a Data Provider, following the establishment of appropriate agreements and access policies.
| Business Process | Status: Proposed |
High Level Requirements
9B.1 - Dataset Processing built-in tool
Simpl shall provide a number of built-in processing tools. In particular ...9B.2 - Data Processing Initiation
Simpl shall provide the Data Consumer with the ability to choose ...9B.3 - Dataset Processing Result storage
The Data Consumer can request to store the results ...9B.4 - Dataset Processing Results
Depending on the access rights and usage policies, as well as ...9B.5 - Dataset source copy
Simpl shall generate a copy of the dataset that is to be processed.9B.6 - Mechanisms to configure and provision VMs
Simpl shall provide the mechanisms to be able to automatically configure ...

Please log in or sign up to comment.